The
New Europe
The
European Union: The Evolution of
the Dream


Evolution from
A customs union of 6 countries to
An unprecedented level of economic and political integration of 27
countries (2012)
How?
Gradual Change
Bold Experimentation
Flexibility
Treaty of Paris
Purpose: Purpose: to reduce economic (and, hence, military)
competition in coal and steel industries among original six members by forming
a customs union for coal and steel.
Geographical Scope:
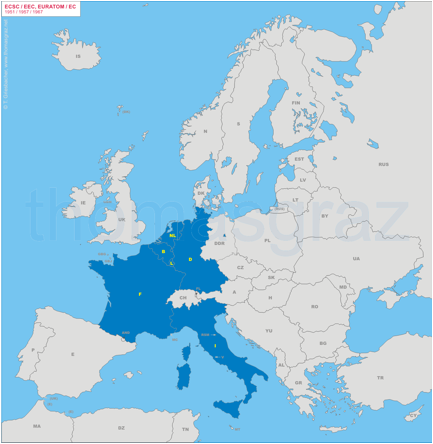
The Original Six –
France
Germany
Italy
Belgium, Netherlands, Luxembourg (collectively referred to as the
BENELUX countries)
1957
Treaty of Rome
Purpose: Est’d European Economic Community
(EEC) and EURATOM along side ECSC
EEC purposes:
1. to expand the ECSC customs union to
other goods
2. elimination of customs duties
3. common external tariffs
4. free movement of labor / capital
5. common policies in agriculture,
transport, competition
EURATOM: cooperation in
peaceful uses of nuclear technology (i.e., energy)
1962 (1963)
1968
Customs union in place
1970
Financial autonomy achieved through:
Customs duties on imports and
Value Added Taxes (VAT)
1970
Foreign Policy Coordination
Regular meetings of foreign ministers begin
1973
Accession of UK, Ireland, Denmark
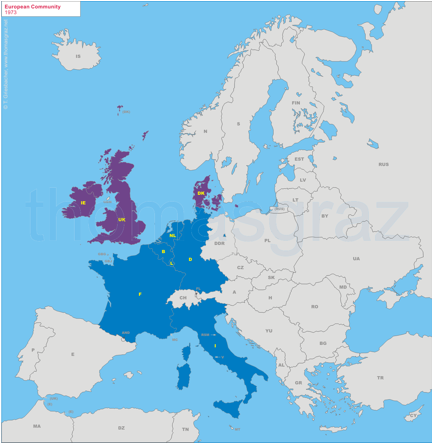
1974
Summits of Heads of State European Council begin
1978
European Monetary System (EMS)
members start to coordinate the value of their
currencies, limit the range of variation between them over time
1981
Accession of Greece
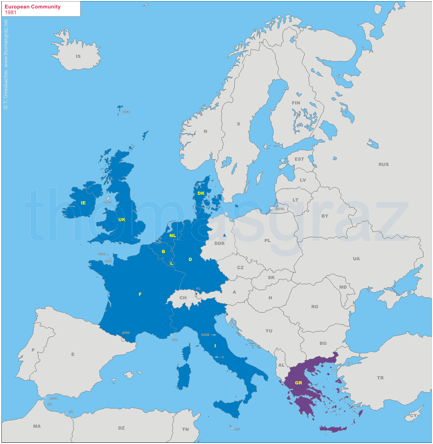
1986
Single European Act
Laid out in White Paper drafted under Commission leadership of
Jacques Delors

Goals:
1.Single market/free trade area to be in
place by 1992
2. eradicate
all NTBs (non-tariff trade barriers)
3.
introduce qualified majority voting at Council
of European Union
1986
Accession of Spain, Portugal
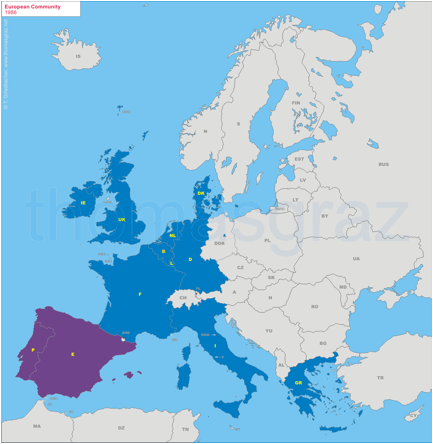
1992
Treaty of the European Union (TEU)
also called the Maastricht Treaty because it was negotiated and signed at
Maastricht, The Netherlands, during the Dutch presidency
Purpose:
Political Integration
Enumerated
3
Pillars of the European Union
Pillar I: European Economic
Communities and Economic and Monetary Union
Set timeline and criteria to adopt
Euro
Pillar II: Common Foreign and Security Policy (CFSP)
Pillar III: Judicial
and Home Affairs
visas, asylum, border control
fighting
international crime, trafficking
TEU also introduced:
An enhanced role for the European Parliament
Co-decision with Commission in some areas
1997
Treaty of Amsterdam
Four
Main Areas of Emphasis
1. Citizens Rights
2. Borders – no internal; stronger
external
3. A Stronger Voice in World Affairs
4. Decision Making
to be Streamlined
with
an eye toward expansion
1995
Accession of Austria, Sweden, Finland
(Norway referendum
fails)
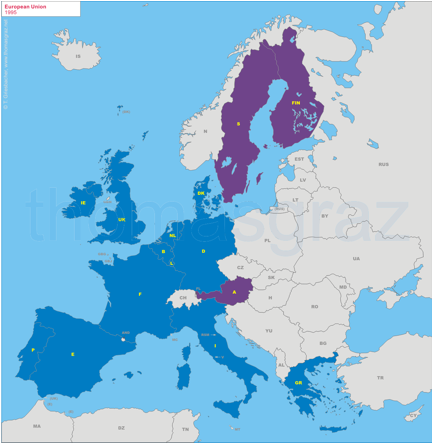
2001
Treaty of Nice drafted (into effect in 2003)
Capped
the number of MEPs at 732; reapportioned
Changed
the rules for Qualified Majority Voting (QMV) at the Council level
Double
majority of member states and percentage of population
Reduced the Commission representation of the larger
states from 2 to 1 Commissioner
2004
Accesssion of Cyprus, Czech Republic, Estonia,
Hungary, Latvia, Lithuania, Malta, Poland, Slovakia,
Slovenia
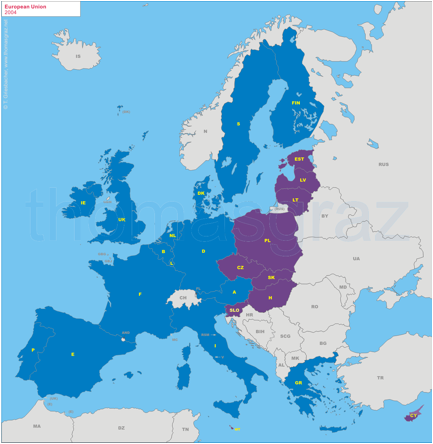
2004-5
EU Constitution
Drafted then Rejected in French, Dutch Referenda
Widely believed to be a referendum on
“Europe,” i.e., supra-nationalism
Especially scorned:
references to EU flag, anthem
2007
Accession of Romania, Bulgaria
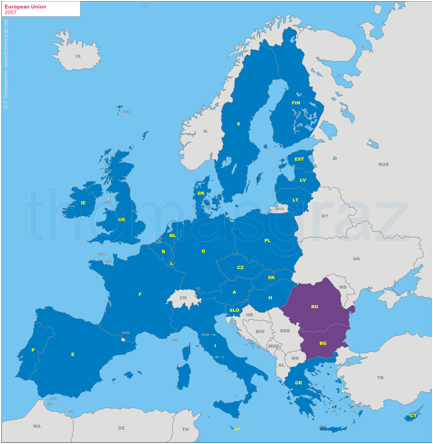
2007
The
Lisbon Treaty aka The Reform Treaty
Got
rid of the symbols, preamble, principles
Kept
the substance, “amends the treaties”
A 2 ½ year European Presidency
And
a EU Foreign Minister
Rejected
first time by Irish voters in referendum
Enter
2008 Financial Crisis!!
2008
Applicant Countries
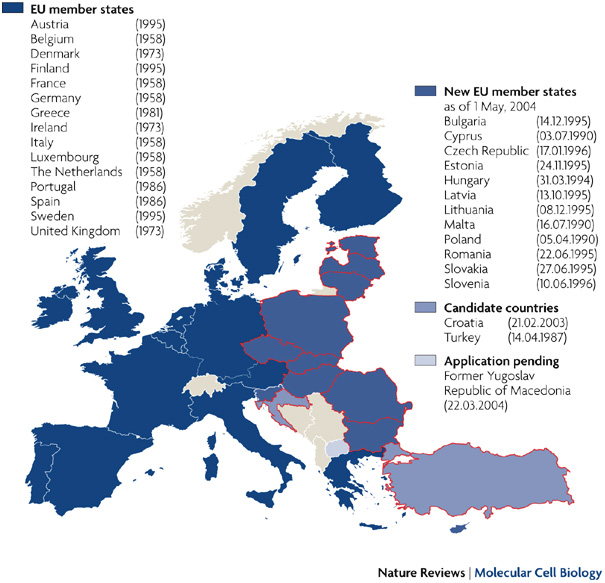
The EU Today
BOTH
an intergovernmental AND a supranational institution
Sovereignty
resides with the nation-states in some areas
Has
been transferred to the EU level in other areas